Augmented brain monitoring solution for general anesthesia to reduce the risk of postoperative complications
Description
Names of partners involved
AP-HP, Inria (équipe-projet MIND, ex PARIETAL)
-
Main objectives
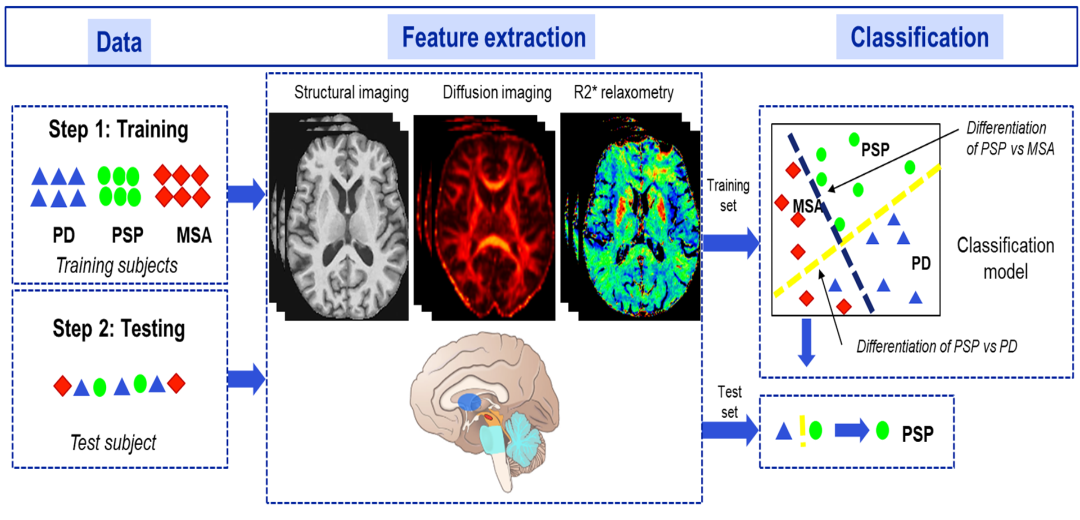
Challenge
Methodology/Technology used
Publications
Members
Augmented brain monitoring solution for general anesthesia to reduce the risk of postoperative complications
Names of partners involved
AP-HP, Inria (équipe-projet MIND, ex PARIETAL)
Innovation Chair “Augmented Operating Room”
Names of partners involved
AP-HP, Inria, Institut Mines-Télécom, Université de Paris-Saclay, Chaire Humanité et Santé du CNAM